April 26, 2010 | Posted by
admin | Category: Linux Administration
How to check Memory (RAM) usage in Linux OR different ways to check RAM usage in Linux?
Memory OR widely known as RAM is known to be one of the important component on the server which make sure the tasks performed on your server are processed fast enough. Higher the availibility of physical memory, more stable is your server during high resource usage processes.
Linux offer various tools to check Memory/RAM usage of your server such as free, top, sar, vmstat etc using which you can deside whether to optimize softwares to use less memory OR whether it’s time to upgrade memory on the server.
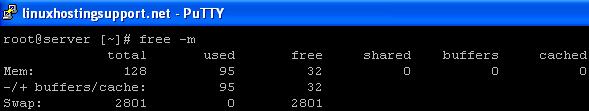
1) ‘free’ command: one of the easiest way to check the RAM usage:
free -m
will display physical memory as well as Swap
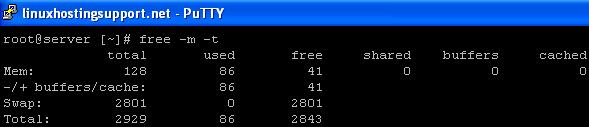
free -m -t
same as above but it will display the total of physical and swap memory at the bottom.
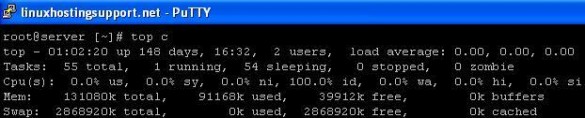
2) ‘top’ command: The top command displays the real time values of the running system and are continously updated (by default 3 seconds). The two rows “Mem and Swap” displays the total, used and free amount of RAM/Swap. Though the values displayed are in kbs and not human readable, it is just one another way to check the usage.
3) ‘sar’ command: is included in the ‘sysstat’ package and is not installed by default. To install ‘sysstat’ package, execute:
yum install sysstat
Once ‘sysstat’ package is installed, start the service
service sysstat start
sysstat package when installed, provider ‘sar’ command which collects system activity information and saves it in a file before displaying it on a standard output.
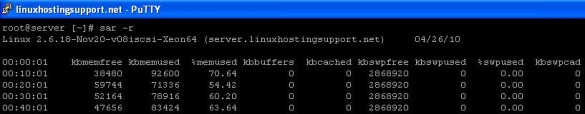
sar -r
displays Memory/Buffer/Swap information horizontally.
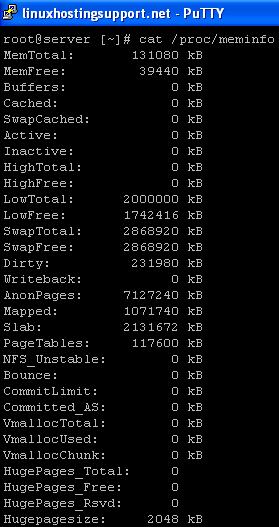
4) /proc/meminfo file: which displays everything about the RAM on your server.
cat /proc/meminfo
Related Links:
Once ‘sysstat’ package is installed, start the service
service sysstat start
Comments Off on Howto: Check Memory/RAM usage in Linux
April 9, 2010 | Posted by
admin | Category: Linux Administration
If the db4 packages (db4 and db4-devel) are missing on the server it results in “version.c:30:16: error: db.h” error message while installing any package. The error looks like:
version.c:30:16: error: db.h: No such file or directory
make: *** [version.o] Error 1
See if the db4 packages are installed
# rpm -qa | grep db4-devel
db4-4.2.52-7.3.el4
db4-devel-4.2.52-7.3.el4
If the above commands returns nothing, you have to install the db4 and db4-devel packages. Search the packages using yum and it should list both of them:
# yum search db4
It will list both the db4 and db4-devel packages
db4.x86_64
db4-devel.x86_64
Now, install them
# yum install db4.x86_64
# yum install db4-devel.x86_64
Comments Off on version.c:30:16: error: db.h: No such file or directory
April 5, 2010 | Posted by
admin | Category: Linux Administration
The error message “Starting sshd: Privilege separation user sshd does not exist FAILED” is received on restarting the SSHD service. It indicates that the user ‘sshd’ does not exist. To fix the add the ‘sshd’ user on the server.
If it’s a VPS, your hosting provider can login through the main server and fix it. If it’s a dedicated server, you have to add the user via single user mode unless you were already logged in before the problem occurred.
Add the following to the /etc/passwd file
sshd:x:74:74:Privilege-separated SSH:/var/empty/sshd:/sbin/nologin
add the below line to /etc/group file
sshd:x:74:
Restart the sshd service.
# /etc/init.d/sshd restart
Stopping sshd: [ OK ]
Starting sshd: [ OK ]
An alternate solution is to disable UsePrivilegeSeparation in the SSHD configuration. Edit the file /etc/ssh/sshd_config and change
UsePrivilegeSeparation yes
to
UsePrivilegeSeparation no
It is less secure but just another option.
Comments Off on Starting sshd: Privilege separation user does not exist
March 19, 2010 | Posted by
admin | Category: Linux Administration
SSH service can be secured in various ways like changing the SSH port, changing the ssh protocol, ssh ListenAddress, disable root login with the PermitRootLogin parameter, allowing ssh access to specific users, restricting SSH access to specific IPs etc. These steps will make sure SSH service on your server is secure.
Edit the SSHD configuration and make the changes listed below:
vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config
1) Set the default SSH port 22 to a higher value, by changing the ‘Port’ directive
Port 2233
2) To make SSH work on a secure protocol, set the ‘Protocol’ directive as
Protocol 2
3) Bind SSHD service to a specific IP of the server, which you can achieve by replacing ‘#ListenAddress’ directive to
ListenAddress xx.xx.xx.xx
where, xx.xx.xx.xx is the additional IP of the server and the only one which will allow you to SSH into the server.
4) To disable root access, set ‘PermitRootLogin’ directive to ‘no’
PermitRootLogin no
Make sure you add an alternate SSH user on the server who have privileges to gain root access before disabling this option.
5) To allow SSH access to specific users, add the “AllowUsers” directive at the end of the configuration
AllowUsers user1 user2
This will allow SSH access to users user1 and user2. You need to allow SSH access to the user who is allowed to gain root access incase root access is disabled.
Save the file and restart the sshd service
service sshd restart
6) Using the TCP wrappers i.e. hosts.allow and hosts.deny, you can restrict SSH access to specific IPs i.e. edit /etc/hosts.allow and add the following
sshd : yourlocalip: allow
sshd : all : deny
“yourlocalip” is the one assigned by your ISP. It will restrict SSH access to your local IP only.
Comments Off on How to secure the SSHD service?
March 9, 2010 | Posted by
admin | Category: Linux Administration
Error:
VFS: Error -5 occurred while creating quota.
VFS: find_free_dqentry(): Data block full but it shouldn't.
Explanation:
When the quota files i.e. aquota.user and aquota.group gets corrupt, you will notice the server logs with a message “VFS: Error -5 occurred while creating quota. find_free_dqentry(): Data block full but it shouldn’t”.
The ‘fixquotas’ script is use to update the quota files but the script cannot read these files either thus increases the CPU usage while quota update is in process. The solution is to remove and create the aquota.user and aquota.group files and run the quotacheck again.
Solution:
First, turn off the quota:
# quotaoff -av
Move the aquota files i.e. /aquota.user and /aquota.group to a temporary directory.
# mkdir /root/tmp_aquota
# mv /aquota.* /root/tmp_aquota/
Now, create the aquota.user and aquota.group files again
# touch /aquota.user
# touch /aquota.group
Now, execute ‘quotacheck’ to build a table of current disk usage.
# /scripts/quotacheck (cPanel server)
OR
# quotacheck -augm
While quotacheck in process, you may see a message as “quotacheck : Warning quota files aquota.group was probably truncated. Can’t save quota settings” which is normal under these circumstances.
Once the quotacheck process completes, turn on the quotas
# quotaon -av
Quota update will work fine again.
Comments Off on find_free_dqentry(): Data block full but it shouldn’t.




