May 10, 2010 | Posted by
admin | Category: Linux Administration
The ‘mock’ module is responsible to build the source RPMs (SRPMs) under a chroot environment and uses the ‘mockbuild’ user.
If the mockbuild user does not exist while installing the source RPM, you will receive the ‘Warning: user mockbuild does not exist. using root‘ error message.
In order to fix the warning message, install the ‘mock’ module:
# yum install mock
and create the ‘mockbuild’ user
# useradd -s /sbin/nologin mockbuild
Once done, you should be able to install the required tool under the mockbuild user.
May 7, 2010 | Posted by
admin | Category: cPanel Management
When Apache is compiled as CGI/SuPHP, it allows users to create their own php.ini file under their home directory and modify the php values as per their wish.
This may increase security concerns on the server and hence to protect/secure php.ini in SuPHP enabled servers, force every user to use a common php.ini file.
This can be achieved by defining the path of server side php.ini file using suPHP_ConfigPath directive. To force users to use server side php.ini file, create suphp_configpath.conf
# pico /usr/local/apache/conf/userdata/suphp_configpath.conf
and add the following lines
<IfModule mod_suphp.c>
<Location />
suPHP_ConfigPath /usr/local/lib/
</Location>
</IfModule>
Once done, save the file and rebuild the Apache configuration so it picks up the changes.
# /usr/local/cpanel/bin/apache_conf_distiller --update --main
# /usr/local/cpanel/bin/build_apache_conf
To verify the include files, execute:
# /scripts/verify_vhost_includes
It will display the path of the .conf file you created. Restart the Apache service once
# /scripts/restartsrv httpd
This will ensure all the users use the server side php configuration file. If you wish to keep the php.ini elsewhere, just change the value of “suPHP_ConfigPath” and follow the above steps.
Comments Off on How to protect/secure php.ini with SuPHP?
May 2, 2010 | Posted by
admin | Category: Linux Administration
When PHP is not compiled with Mysql, you receive ‘Call to undefined function mysql_connect’ error message on your website
Fatal error: Call to undefined function mysql_connect()
in filename.php on line xx
In order to fix the issue, install the “php-mysql” package using yum
# yum install php-mysql
Once installed, restart the httpd service
# service httpd restart
To verify if the package is installed properly, execute
# php -i | grep mysql
Comments Off on Fatal error: Call to undefined function mysql_connect()
April 26, 2010 | Posted by
admin | Category: Linux Administration
How to check Memory (RAM) usage in Linux OR different ways to check RAM usage in Linux?
Memory OR widely known as RAM is known to be one of the important component on the server which make sure the tasks performed on your server are processed fast enough. Higher the availibility of physical memory, more stable is your server during high resource usage processes.
Linux offer various tools to check Memory/RAM usage of your server such as free, top, sar, vmstat etc using which you can deside whether to optimize softwares to use less memory OR whether it’s time to upgrade memory on the server.
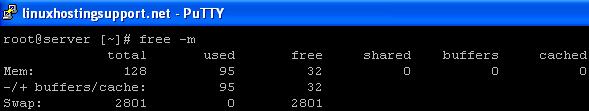
1) ‘free’ command: one of the easiest way to check the RAM usage:
free -m
will display physical memory as well as Swap
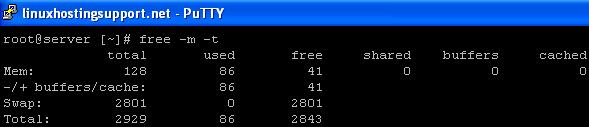
free -m -t
same as above but it will display the total of physical and swap memory at the bottom.
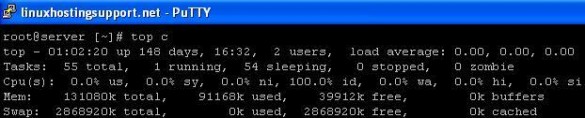
2) ‘top’ command: The top command displays the real time values of the running system and are continously updated (by default 3 seconds). The two rows “Mem and Swap” displays the total, used and free amount of RAM/Swap. Though the values displayed are in kbs and not human readable, it is just one another way to check the usage.
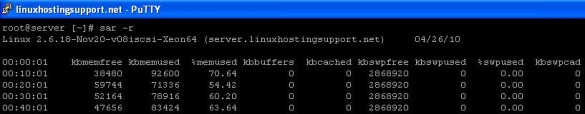
3) ‘sar’ command: is included in the ‘sysstat’ package and is not installed by default. To install ‘sysstat’ package, execute:
yum install sysstat
Once ‘sysstat’ package is installed, start the service
service sysstat start
sysstat package when installed, provider ‘sar’ command which collects system activity information and saves it in a file before displaying it on a standard output.
sar -r
displays Memory/Buffer/Swap information horizontally.
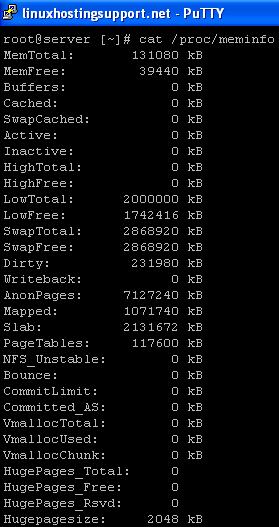
4) /proc/meminfo file: which displays everything about the RAM on your server.
cat /proc/meminfo
Related Links:
Once ‘sysstat’ package is installed, start the service
service sysstat start
Comments Off on Howto: Check Memory/RAM usage in Linux
April 9, 2010 | Posted by
admin | Category: Linux Administration
If the db4 packages (db4 and db4-devel) are missing on the server it results in “version.c:30:16: error: db.h” error message while installing any package. The error looks like:
version.c:30:16: error: db.h: No such file or directory
make: *** [version.o] Error 1
See if the db4 packages are installed
# rpm -qa | grep db4-devel
db4-4.2.52-7.3.el4
db4-devel-4.2.52-7.3.el4
If the above commands returns nothing, you have to install the db4 and db4-devel packages. Search the packages using yum and it should list both of them:
# yum search db4
It will list both the db4 and db4-devel packages
db4.x86_64
db4-devel.x86_64
Now, install them
# yum install db4.x86_64
# yum install db4-devel.x86_64
Comments Off on version.c:30:16: error: db.h: No such file or directory




